User Tools
Sidebar
Recover Your Server
Summary
After restoring the backed up Windows System image from the backup destination, you can use the restored data to recover your server.
For server platforms such as Server 2008 / 2008 R2 / 2012 / 2012 R2, you can recover individual files, folders, volumes, application, application data, operating system, or full-system (bare-metal) with the following tools:
| Tool | What you can recover |
|---|---|
| Recovery wizard (in Windows Server Backup) | Files, folders, volumes, application, and application data. |
| Windows setup disc / Windows Recovery Environment (Windows RE) | Operating system (critical volume), and full server recovery (all volumes). |
You can also perform the above tasks using wbadmin command. For the syntax of the command, refer to the following: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=140216
To determine what can be recovered from your restored system image, enter the following command in an elevated command prompt:
wbadmin get versions
[-backupTarget:{<BackupTargetLocation> | <NetworkSharePath>}]
Example (system image restored to G: volume):
C:\Users\Administrator>wbadmin get versions -backupTarget:g:
wbadmin 1.0 - Backup command-line tool
(C) Copyright 2012 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Backup time: 1/29/2019 10:29 AM
Backup target: 1394/USB Disk labeled Temp1(E:)
Version identifier: 01/29/2019-02:29
Can recover: Volume(s), File(s), Application(s), Bare Metal Recovery, System State
Snapshot ID: {f8cf57da-0c9d-453c-adbb-5f9a976c75c2}
For non-server platforms such as Windows 7 / 8 / 8.1 / 10, you can recover the full-system (bare-metal) with the following tools:
| Tool | What you can recover |
|---|---|
| Advanced startup option (in safe mode) | Full system recovery. |
| Advanced startup option (Windows installation media) | Full system recovery. |
You can also perform the above tasks using wbadmin command. For the syntax of the command, refer to the following: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=140216
For instructions specific to recovering Active Directory Domain Services, refer to the following: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=143754.
Recover Files and Folders
To recover files and folders using the Recovery Wizard in the Windows Server Backup user interface.
1. Open Windows Server Backup from Administrative Tools or Server Manager.
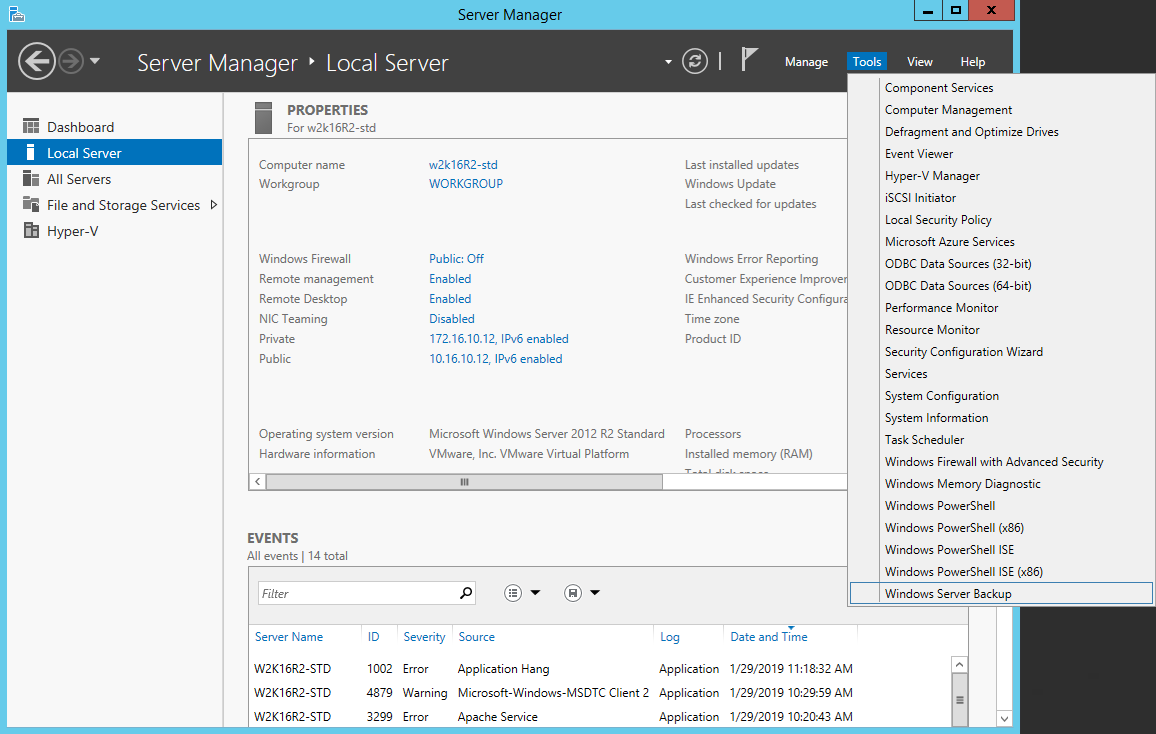
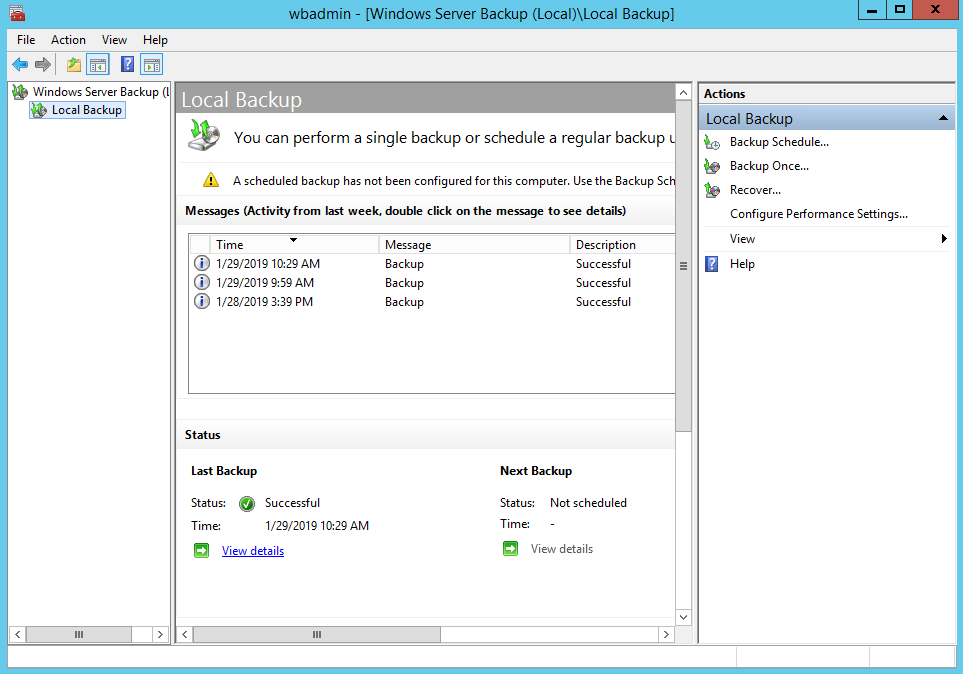
2. In the Actions panel under Windows Server Backup, click Recover…
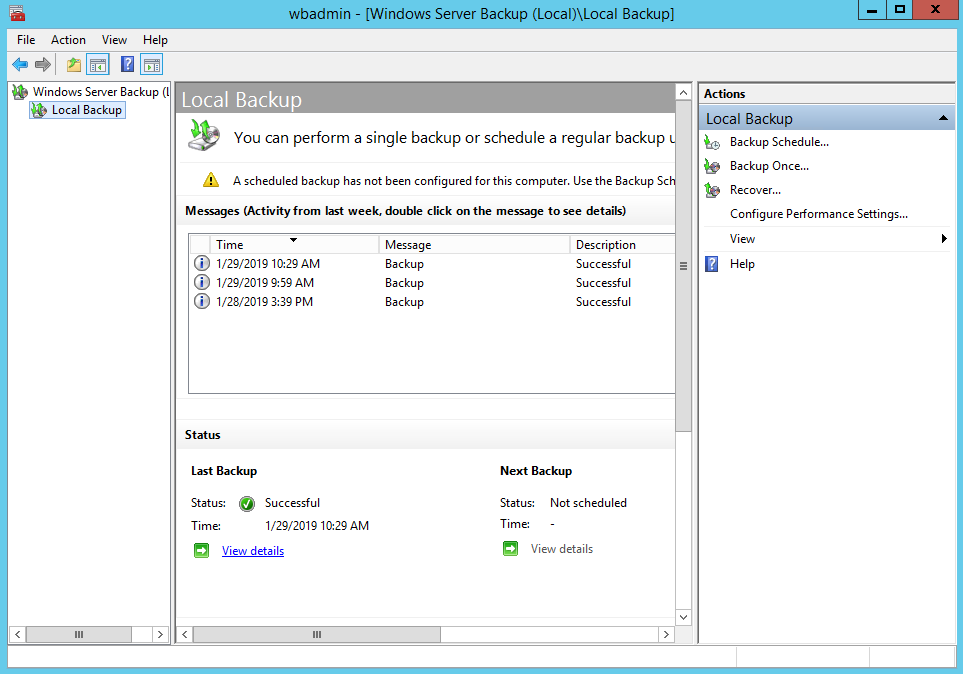
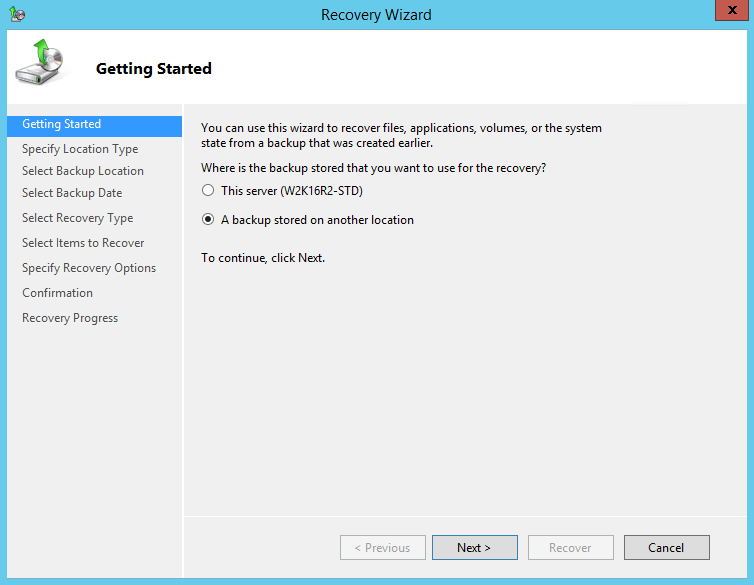
3. On the Getting Started page, select A backup stored on another location, then click Next.
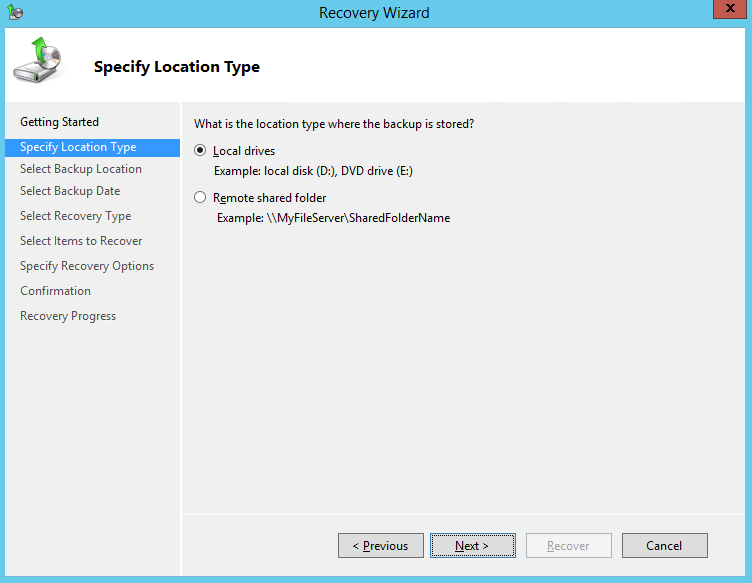
4. On the Specify Location Type page, select
- Click Local drives, if the system image was copied to a local volume on the server.
5. On the Select Backup Location page, select the volume that contains the system image file.

Note: Assuming that the WindowsImageBackup folder was copied to the following F:\ WindowsImageBackup
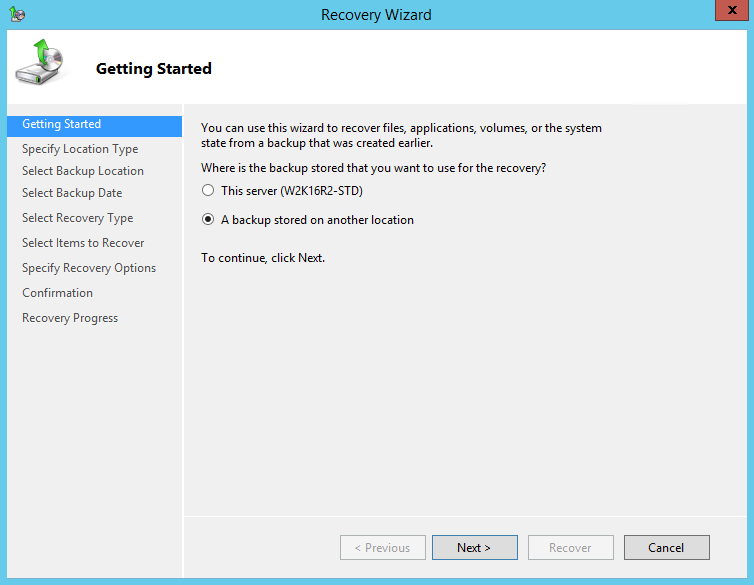
6. On the Select Server page, select the server whose data you want to recover.
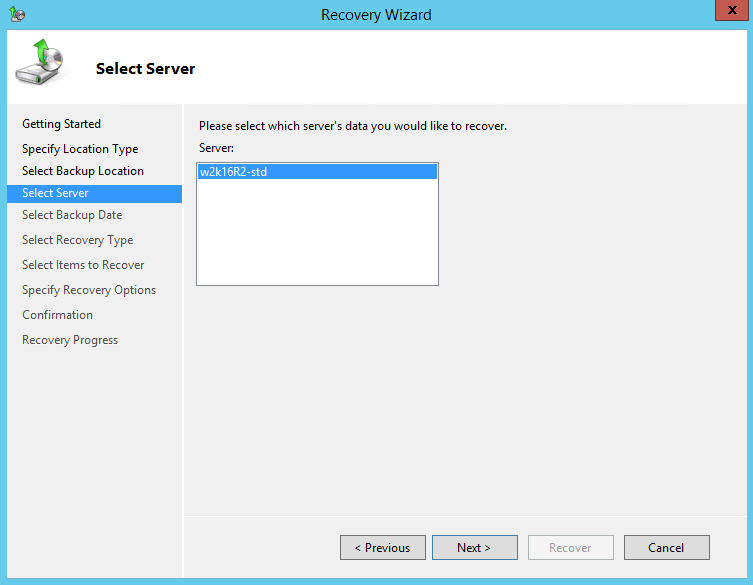
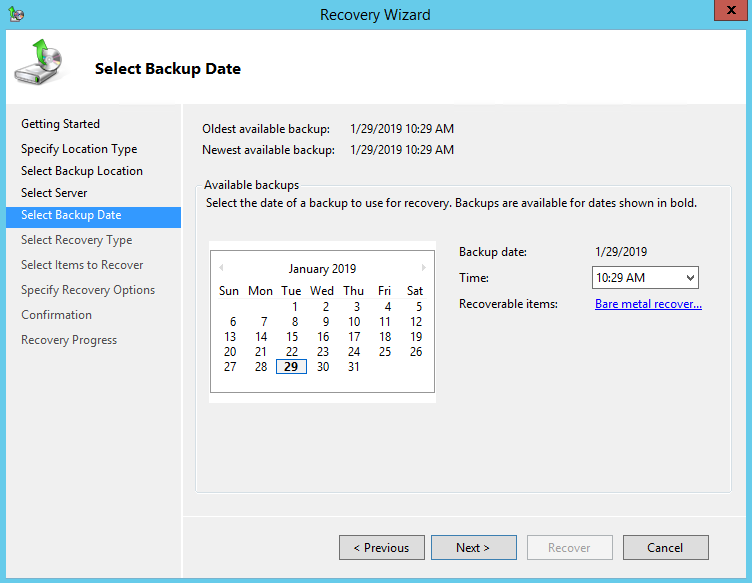
7. On the Select Backup Date page, select the point in time of the backup you want to restore from.
8. On the Select Recovery Type page, click Files and folders.
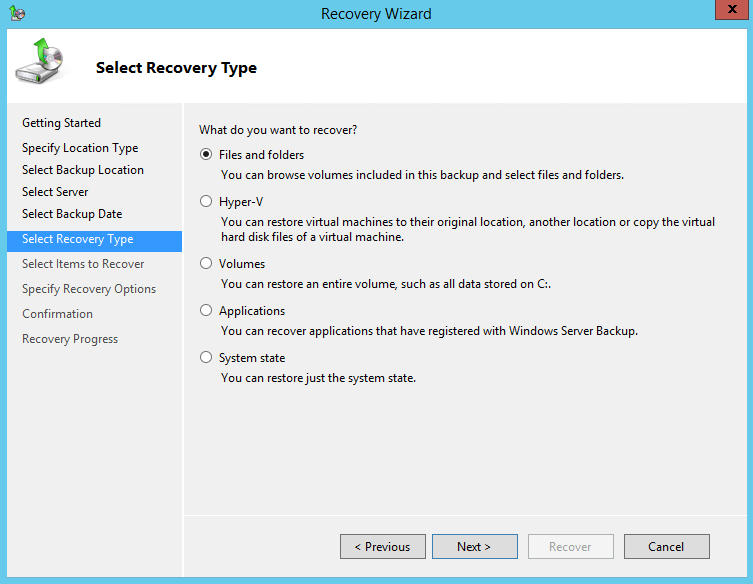
9. On the Select Items to Recover page, under Available items, expand the list until the folder you want is visible.
Click a folder to display the contents in the adjacent pane, click each item that you want to restore.
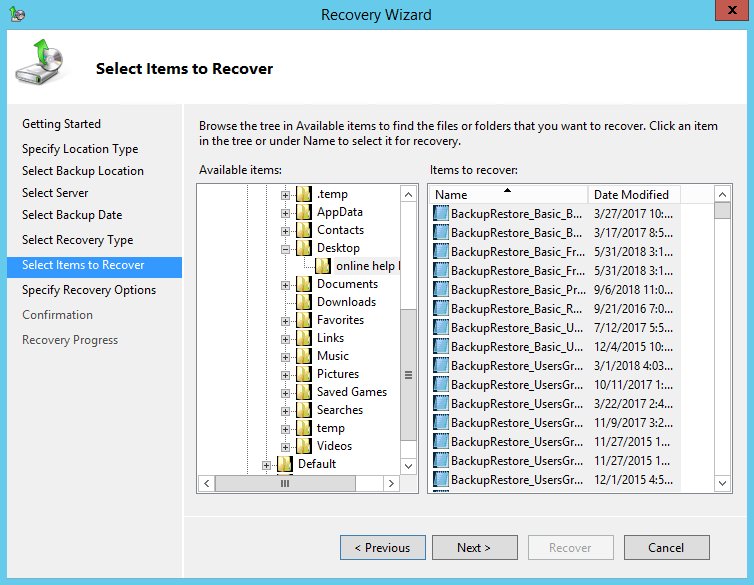
10. On the Specify Recovery Options page, under Recovery destination, select Alternate location.
Type the path to the location or click Browse to select it.

Modify the When this wizard finds items in the backup that are already in the recovery destination setting, and the Security settings if necessary.
Click Next to proceed.
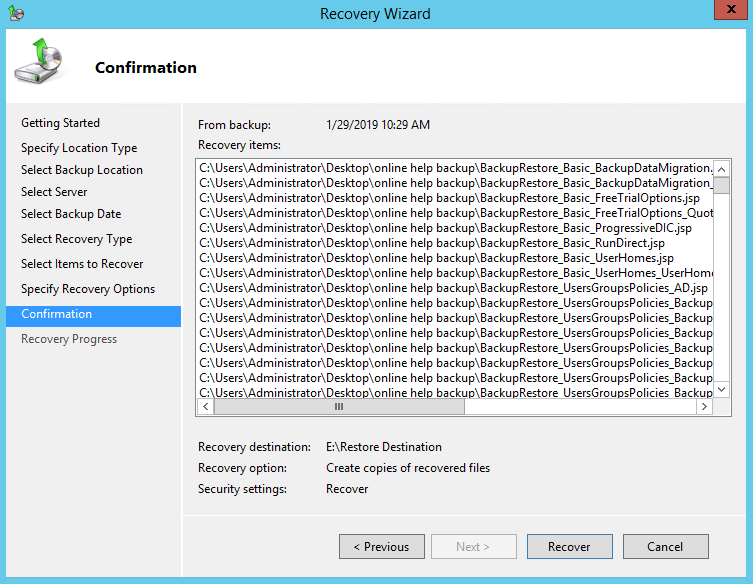
11. On the Confirmation page, review the details, and then click Recover to restore the specified items.
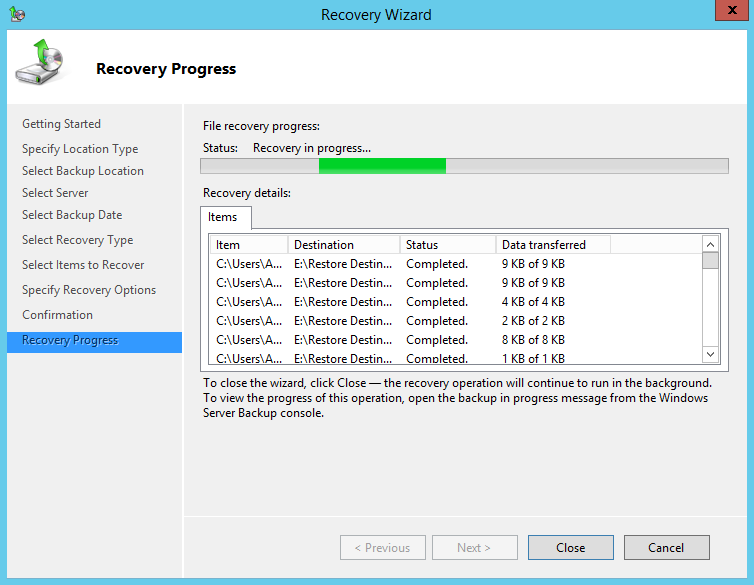
12. On the Recovery progress page, the status and result of the recovery operation is displayed.
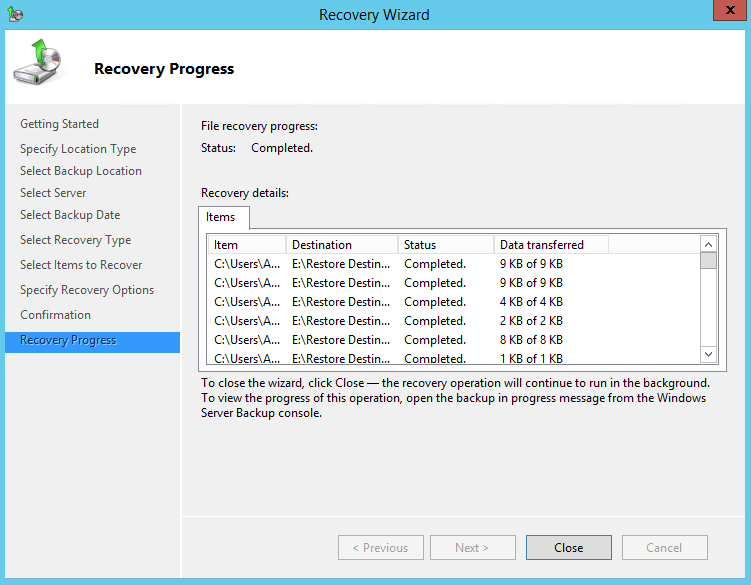
Recover Applications and Data
To recover application and data using the Recovery Wizard in the Windows Server Backup user interface.
1. Open Windows Server Backup from Administrative Tools or Server Manager.
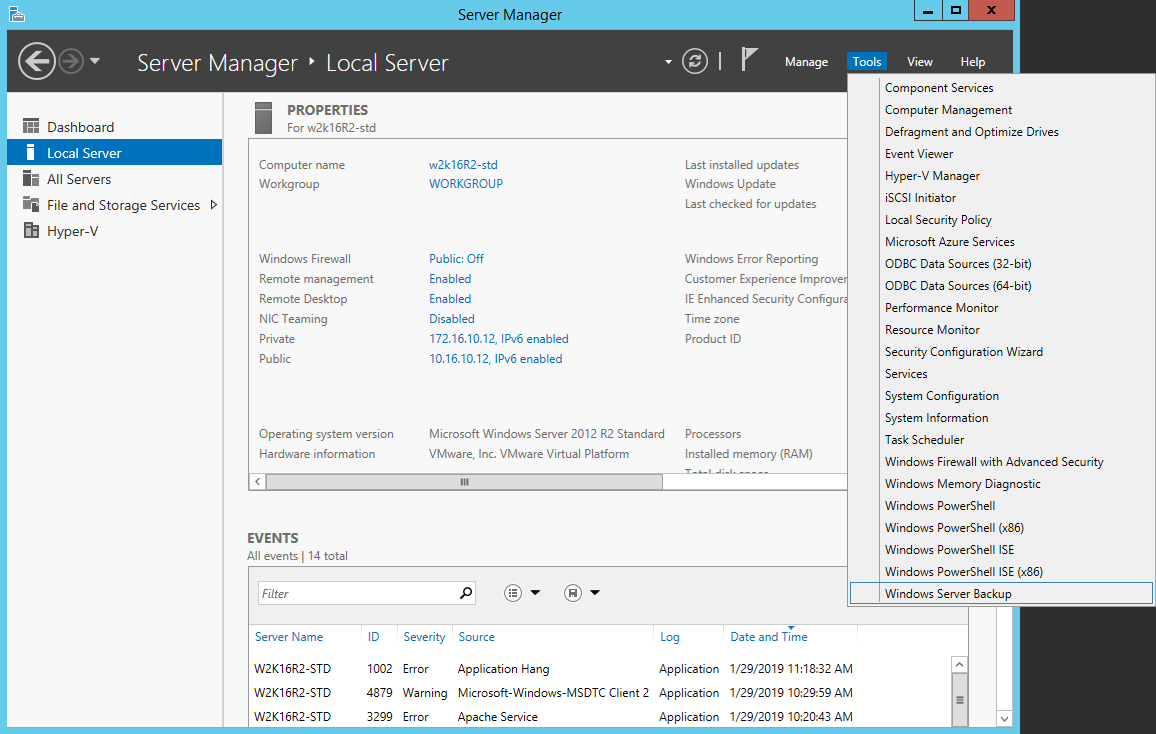
2. In the Actions panel under Windows Server Backup, click Recover…
3. On the Getting Started page, select A backup stored on another location, then click Next.
4. On the Specify Location Type page, select
- Click Local drives, if the system image was copied to a local volume on the server.
5. On the Select Backup Location page, select the volume that contains the system image file.
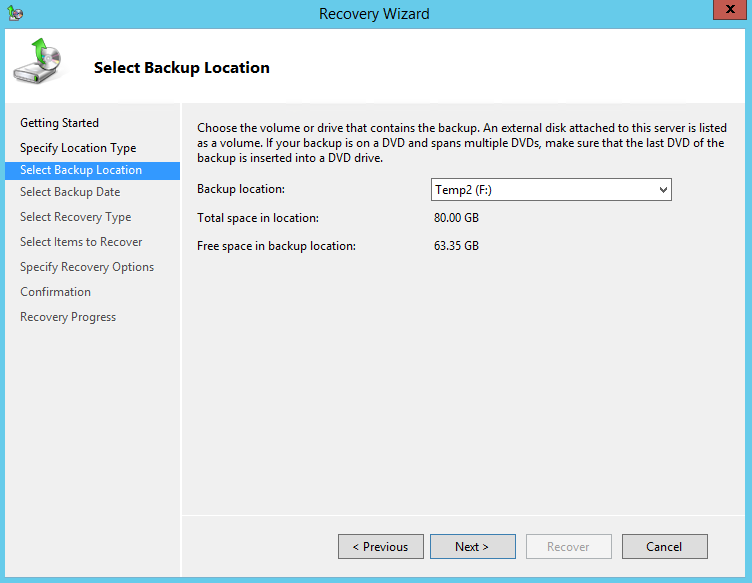
Note: Assuming that the WindowsImageBackup folder was copied to the following F:\ WindowsImageBackup
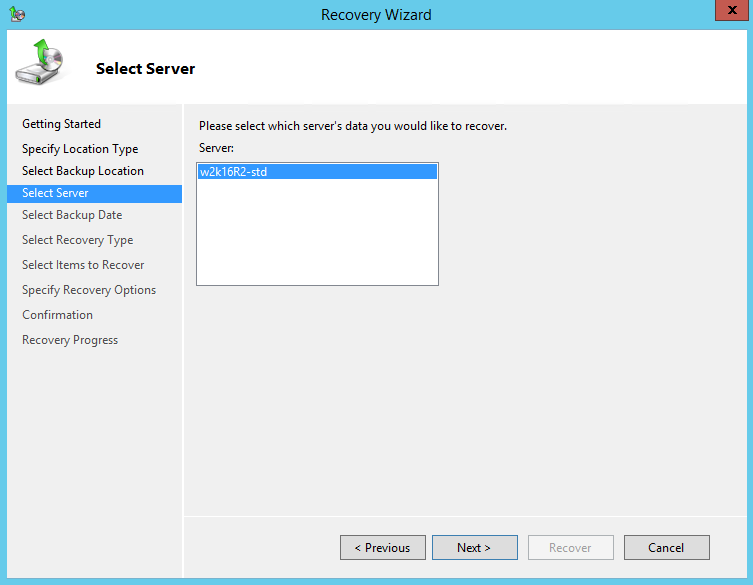
6. On the Select Server page, select the server whose data you want to recover.
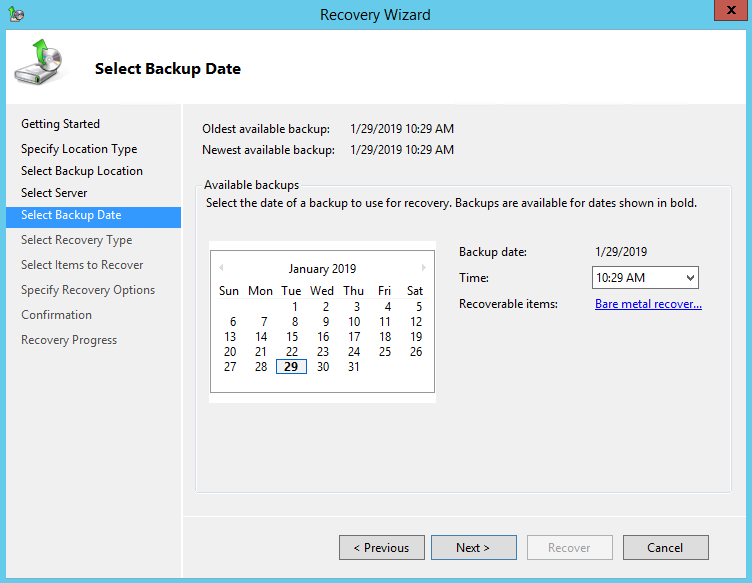
7. On the Select Backup Date page, select the point in time of the backup you want to restore from
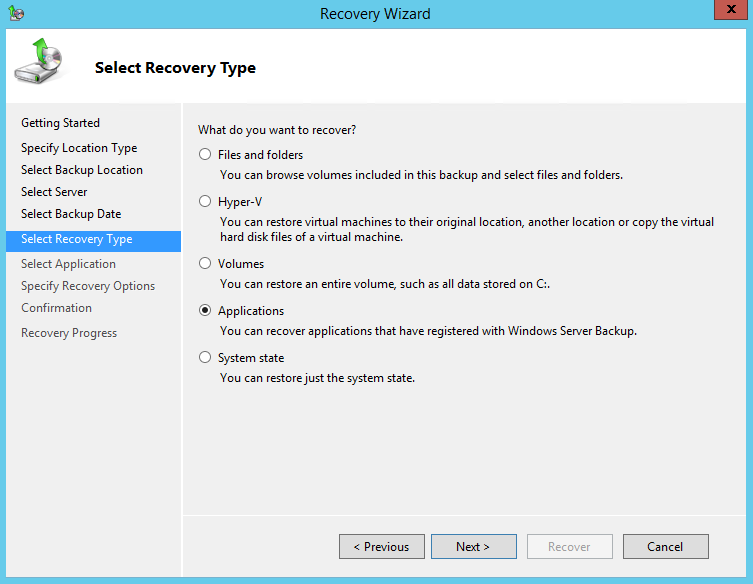
8. On the Select Recovery Type page, click Applications, and then click Next.
9. On the Select Application page, under Applications, click the application that you want to recover.
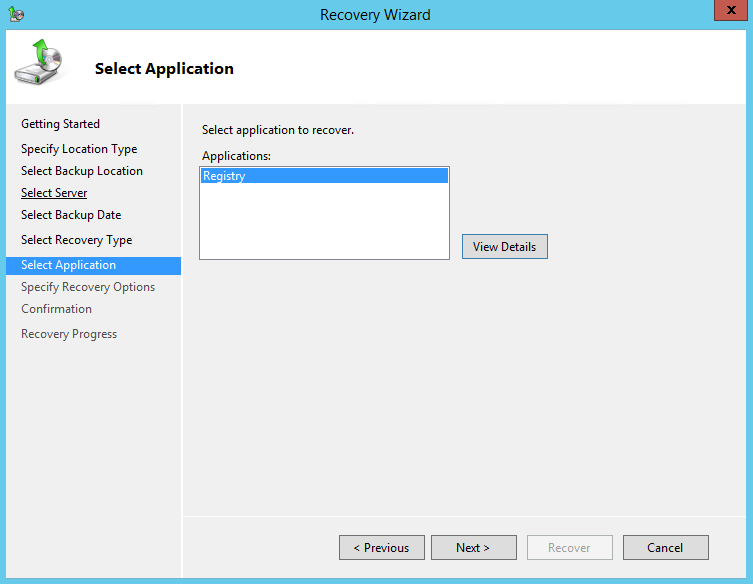
Note: If the backup that you are using is the most recent and the application you are recovering supports a “roll-forward” of the application database, you will see a check box labeled Do not perform a roll-forward recovery of the application databases.
Select this check box if you want to prevent Windows Server Backup from rolling forward the application database that is currently on your server.
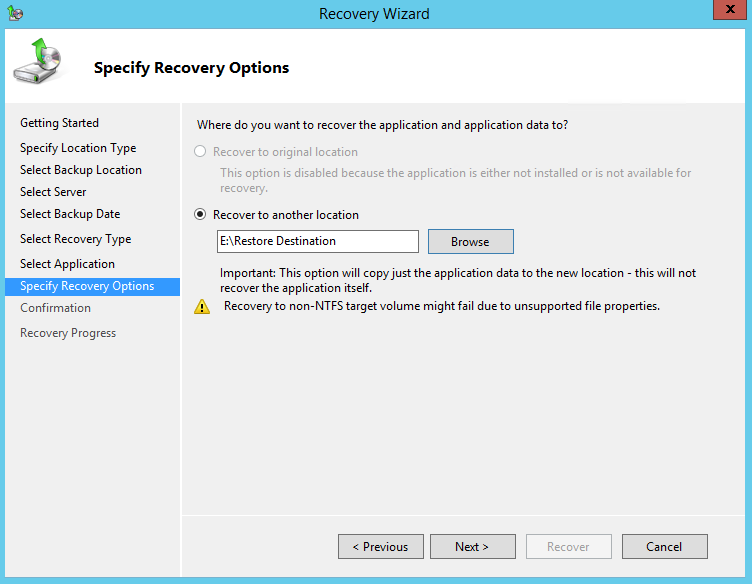
10. On the Specify Recovery Options page, select Recover to another location. Type the path to the location or click Browse to select it.
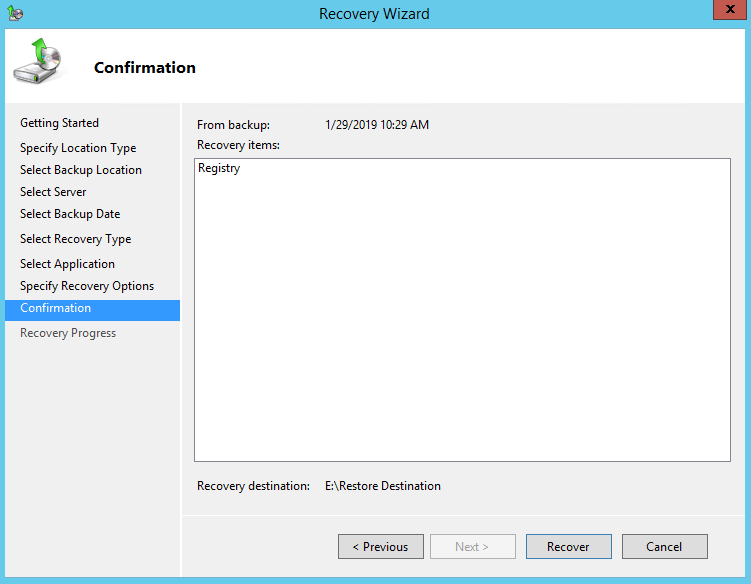
11. On the Confirmation page, review the details, and then click Recover to restore the listed items.
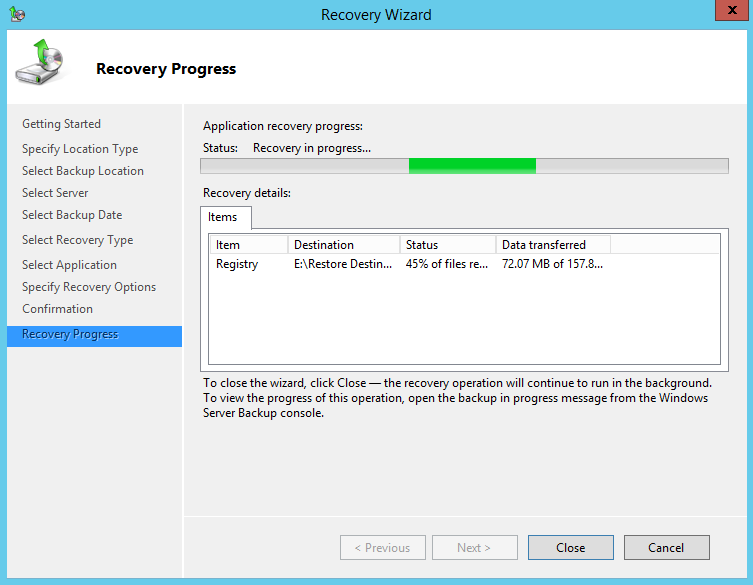
12. On the Recovery progress page, the status and result of the recovery operation is displayed.

Recover Volumes
To recover volume using the Recovery Wizard in the Windows Server Backup user interface.
1. Open Windows Server Backup from Administrative Tools or Server Manager.
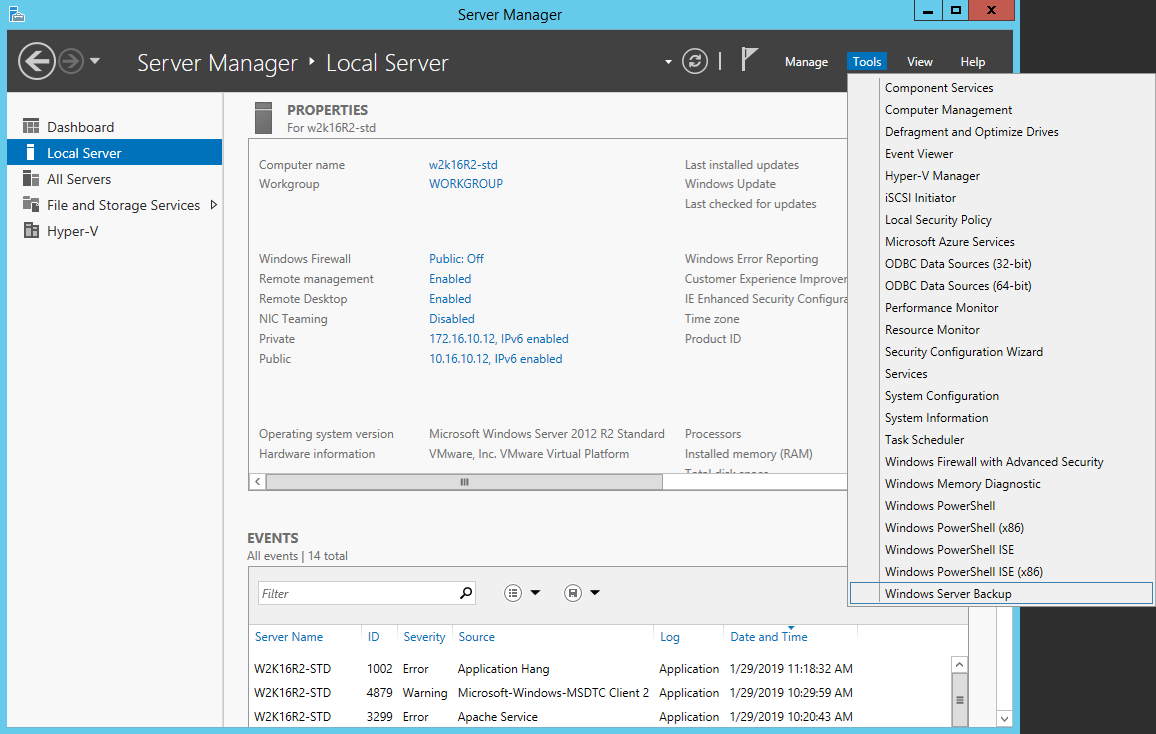
2. In the Actions panel under Windows Server Backup, click Recover.
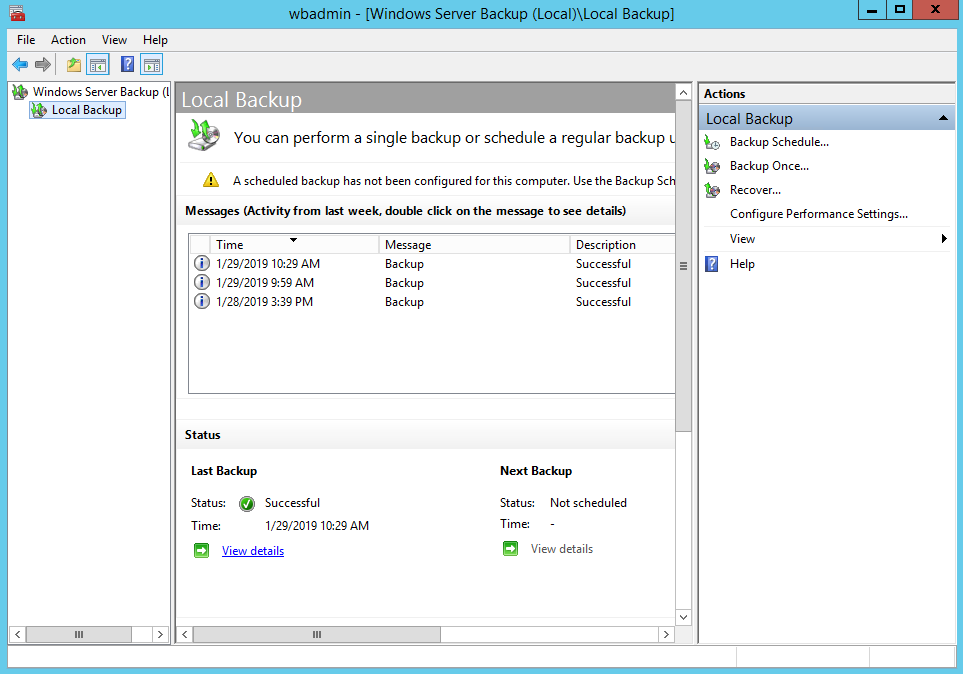
3. On the Getting Started page, select A backup stored on another location, then click Next.
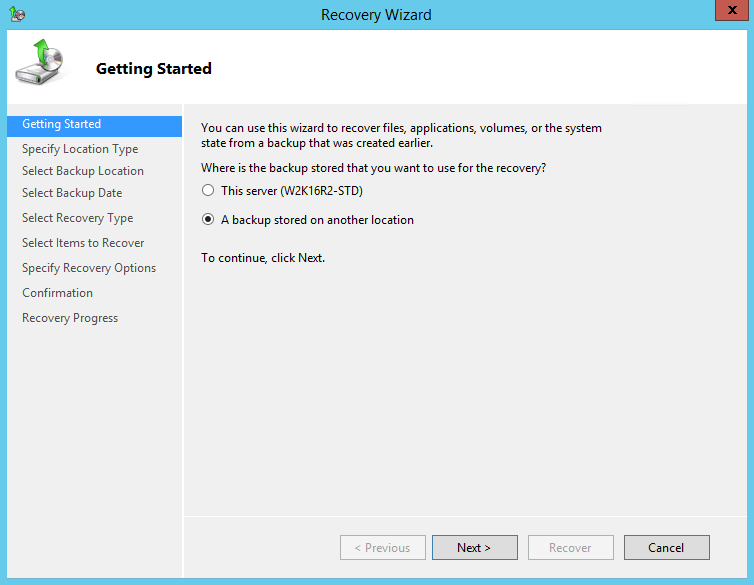
4. On the Specify Location Type page, select
- Click Local drives, if the system image was copied to a local volume on the server.
5. On the Select Backup Location page, select the volume that contains the system image file.

Note: Assuming that the WindowsImageBackup folder was copied to the following F:\ WindowsImageBackup
6. On the Select Server page, select the server whose data you want to recover.
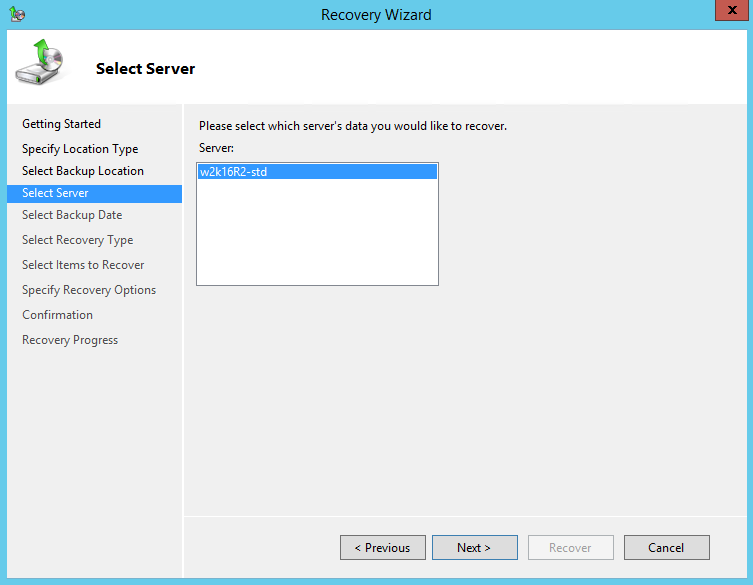
7. On the Select Backup Date page, select the point in time of the backup you want to restore from
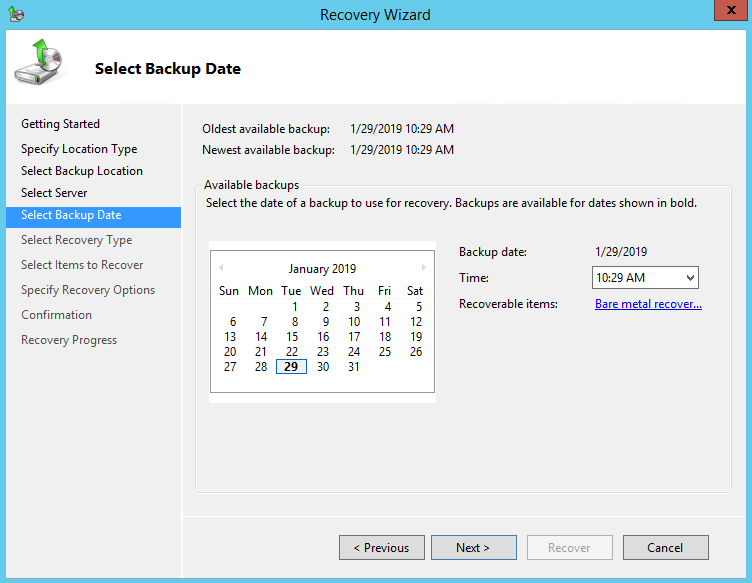
8. On the Select Recovery Type page, click Volumes, and then click Next.
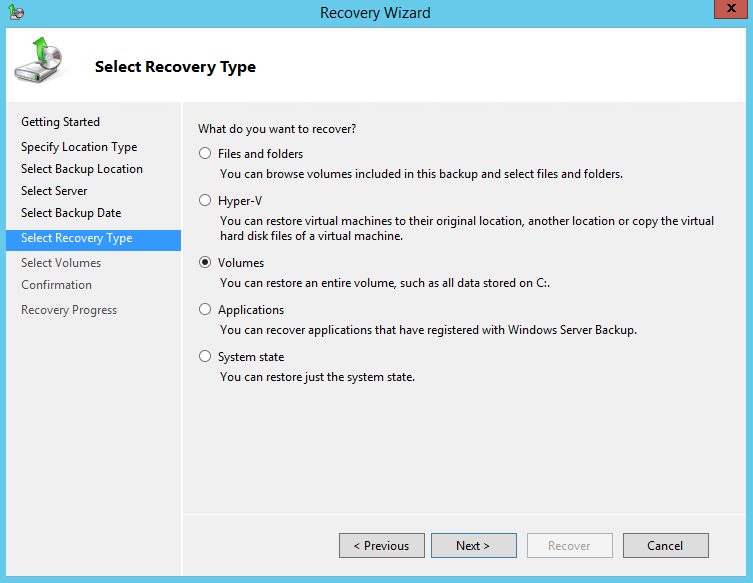
9. On the Select Volumes page, select the check boxes associated with the volumes in the Source Volume column that you want to recover.
Then, from the associated dropdown list in the Destination Volume column, select the location that you want to recover the volume to.

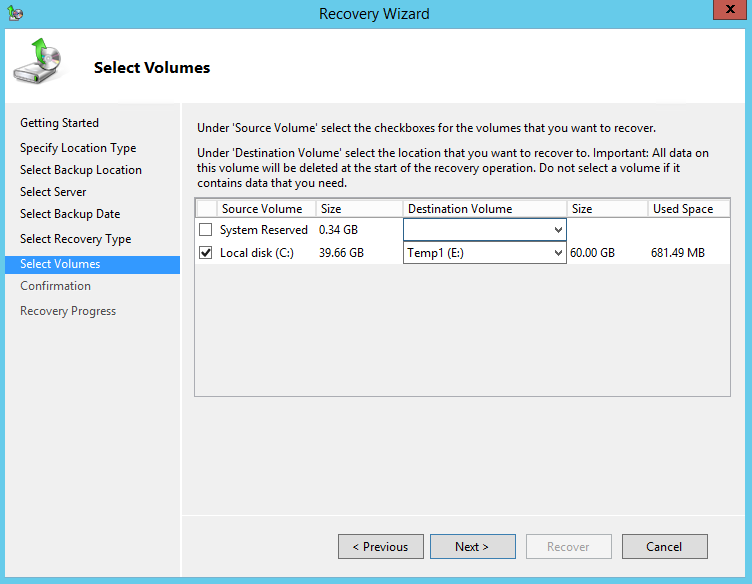
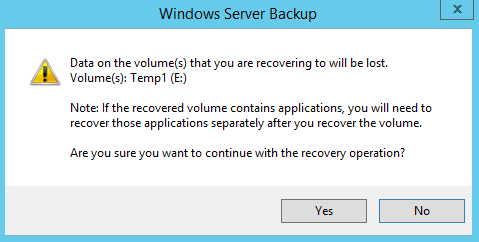
Before clicking Next to continue, make sure that the destination volume is empty, or does not contain information that you will need later.
10. On the Confirmation page, review the details, and then click Recover to restore the volume.

11. On the Recovery progress page, the status and result of the recovery operation is displayed.
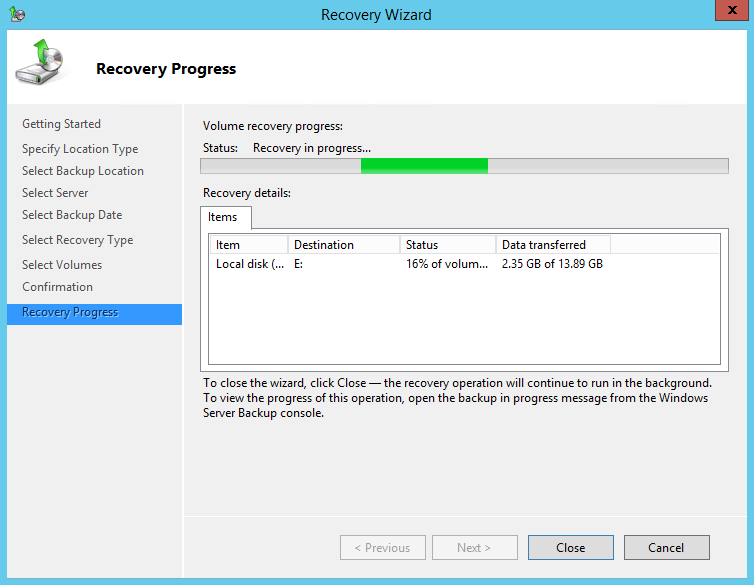
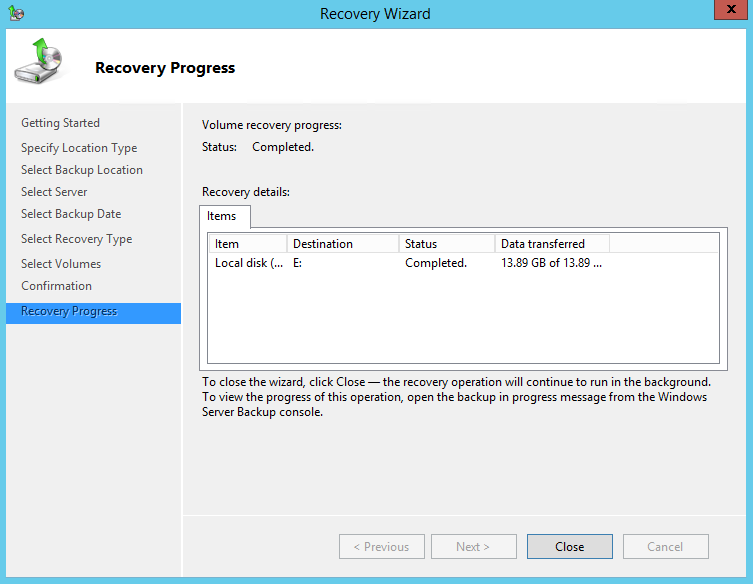
Recover Operating System or Full System
You can recover an operating system or full system by using Windows Recovery Environment, or by booting from a Windows setup disc.
For instructions specific to recovering Active Directory Domain Services, refer to the following: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=143754
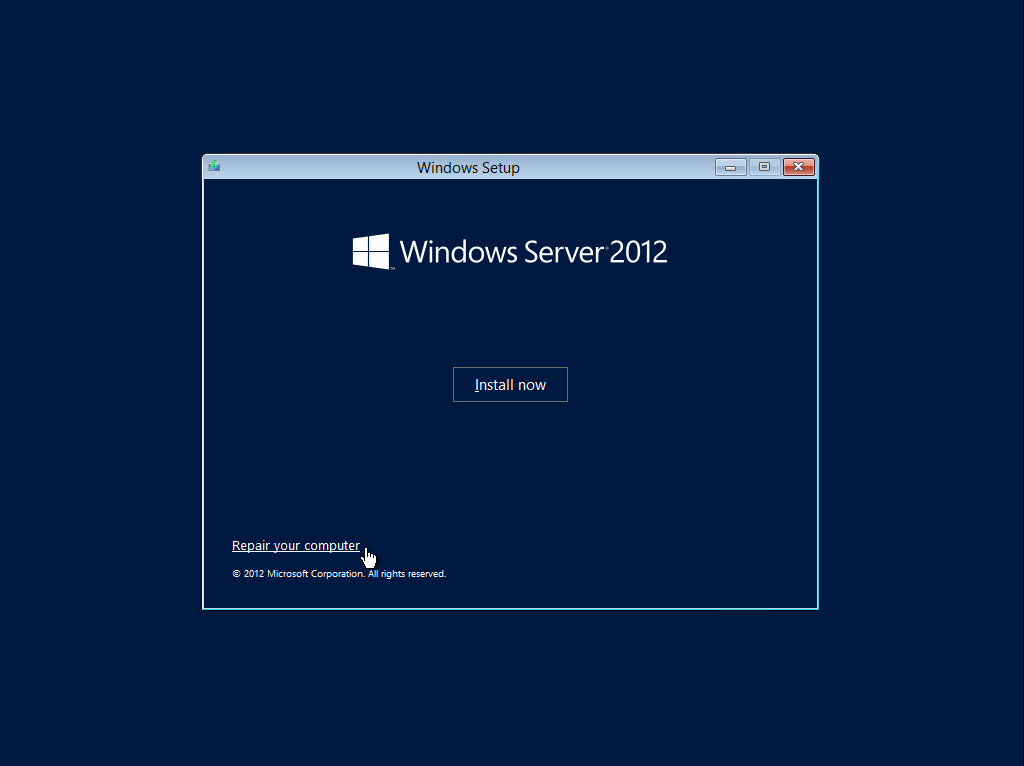
To launch in Windows Recovery Environment, insert the Windows setup disc that has the same architecture of the system that you are recovering, into the CD / DVD drive and start or restart the computer. Press the required key to boot from the disc.
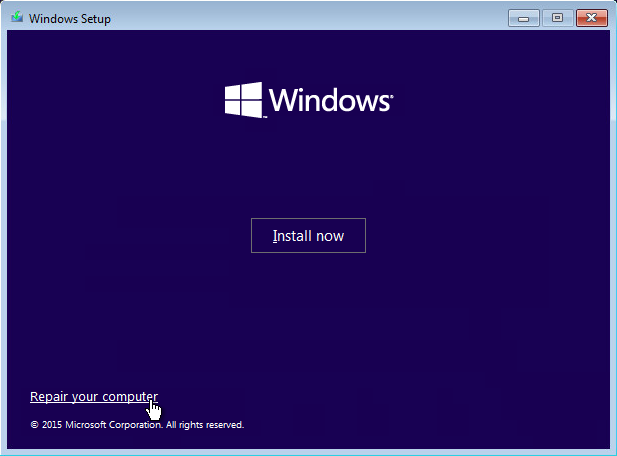
1. On the Windows Setup page, select Repair your computer.
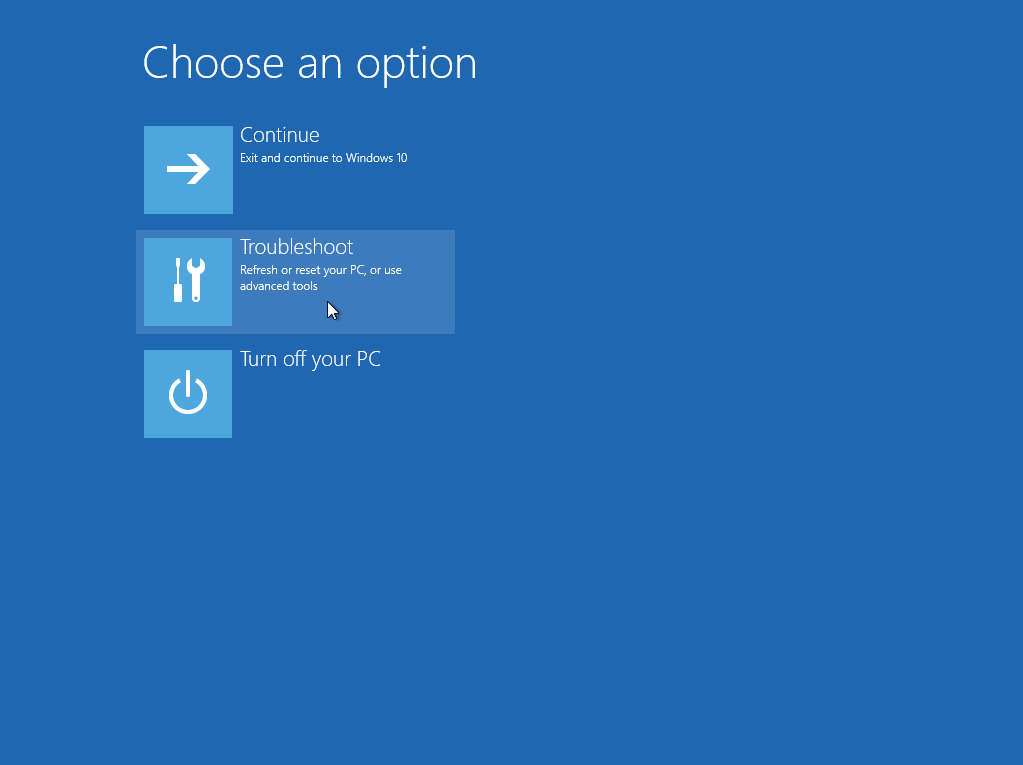
2. On the Choose an option page, click Troubleshoot.
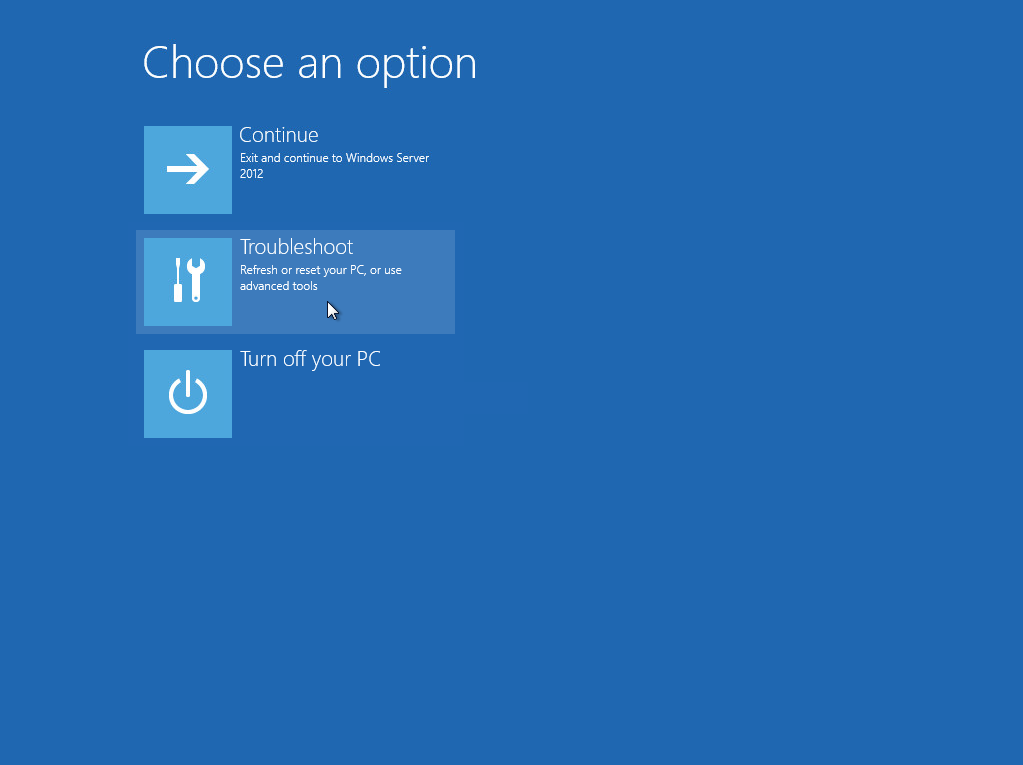
This screen will only be displayed when you are recovering a Windows 2012 / 2012 R2 Server.
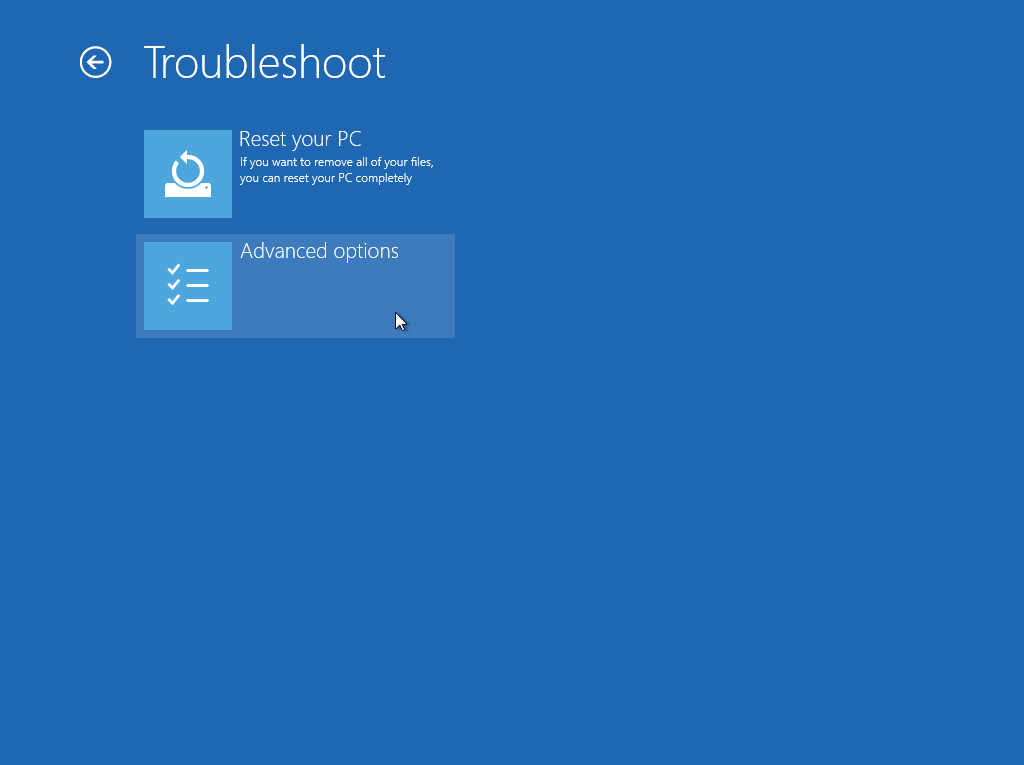
3. Click System Image Recovery.
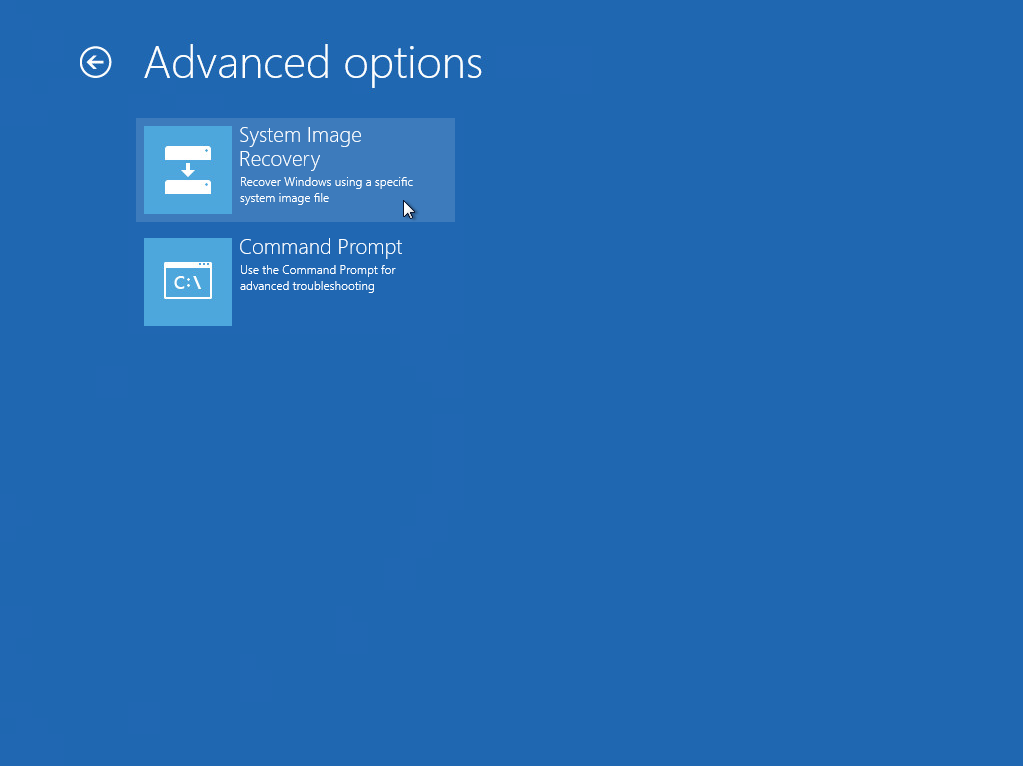
This screen will only be displayed when you are recovering a Windows 2012 / 2012 R2 Server.
4. Confirm on the target operating system. This opens the Re-image your computer page.
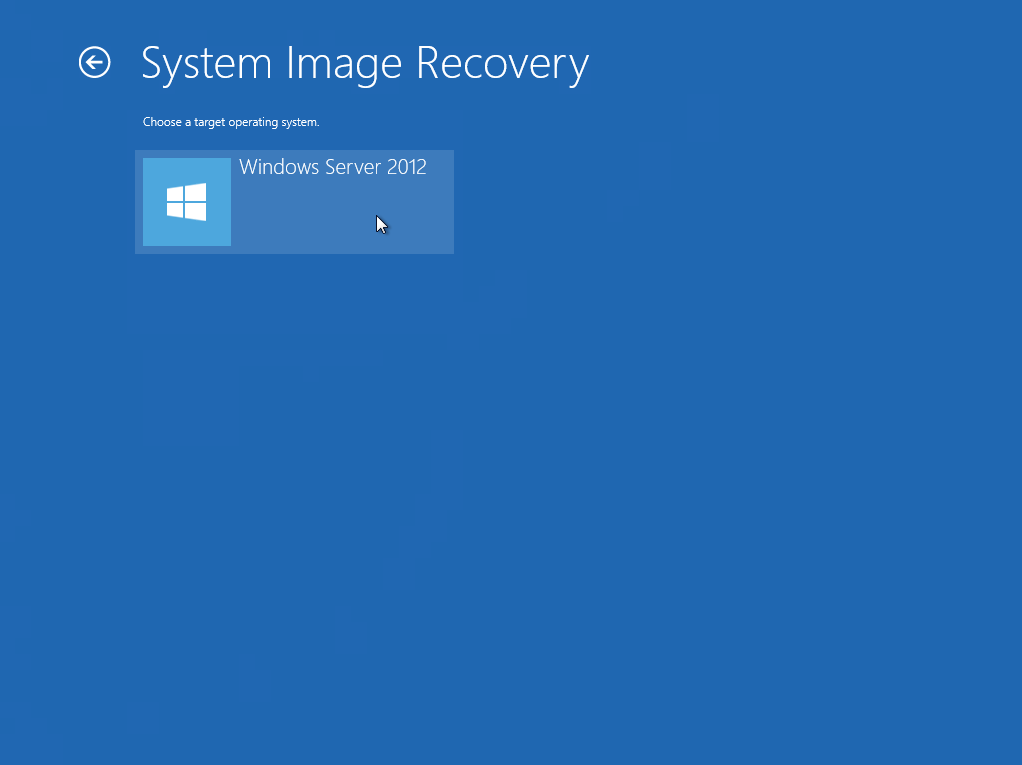
This screen will only be displayed when you are recovering a Windows 2012 / 2012 R2 Server.
5. Click Select a system image, then click Next.
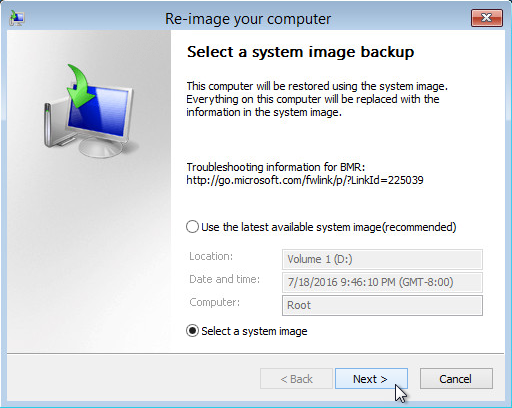
6. Select the location that contains the system image to restore from. If you do not see the image available, then
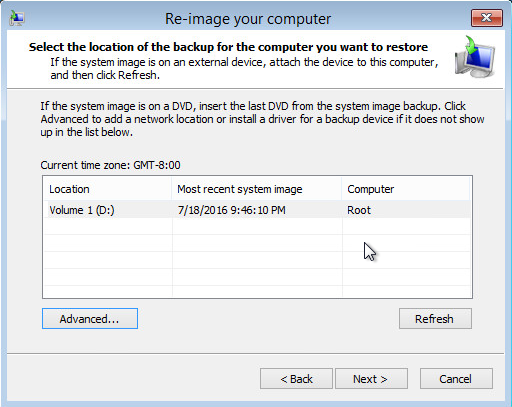
- Click Advanced, and install the required driver for the removable drive to be accessed, if the system image was copied to a removable drive attached to the server.
To install a driver, the driver must be located on the local system. You cannot install a driver from the network.
- Click Advanced, and browse to the remote shared folder which contains the system image, if the system image was copied to a network path.
For domain environment, if the backup storage location is on a computer that is a member of that domain, then the computer containing the storage location should be on the IPsec boundary, to be accessible by non-domain computer.
When a computer boots into Windows Recovery Environment, it becomes a non-domain computer, therefore, cannot access the usual network shares. Only those computers that allow non-domain computers to access the share can be used as a backup storage location in this way.
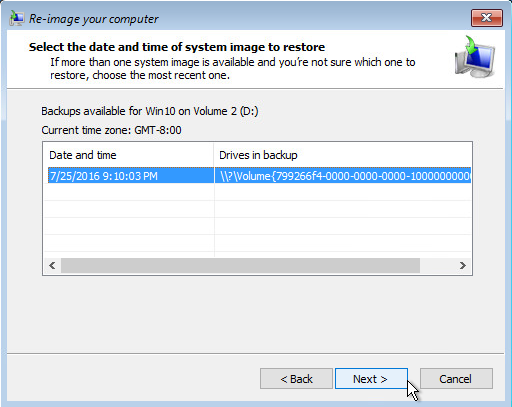
7. Select the date and time of system image to restore.
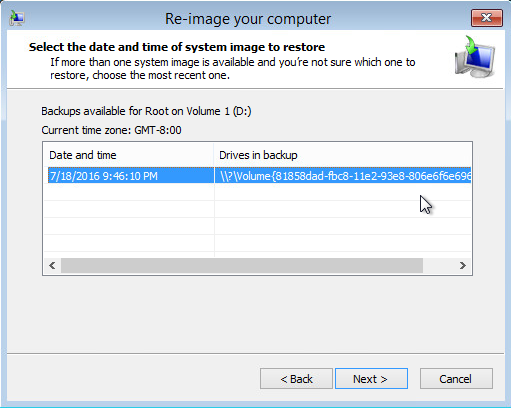
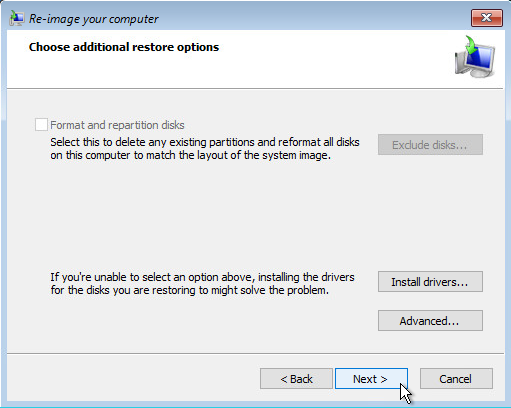
8. On the Choose additional restore options page
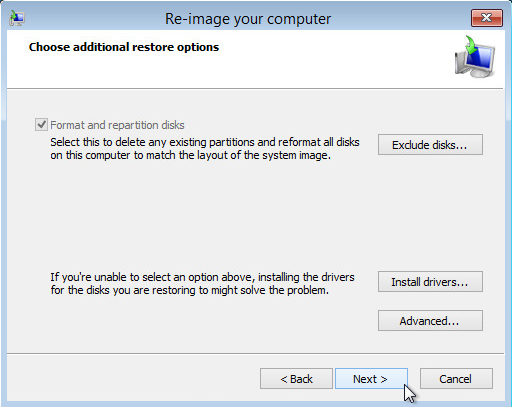
Select the Format and repartition disks check box to delete existing partitions and reformat the destination disks to be the same as the backup.
Click the Exclude disks button, then select the check boxes associated with any disks that you want to exclude from being formatted and partitioned.
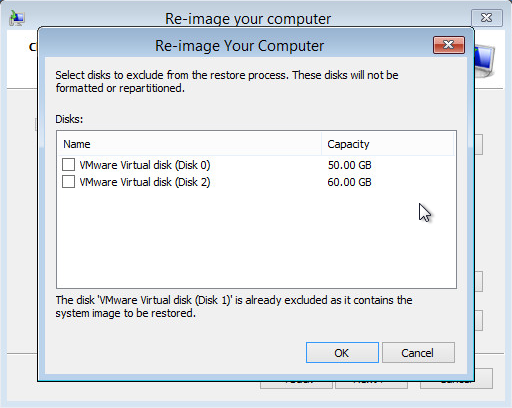
The disk that contains the backup that you are using is automatically excluded.
Select the Only restore system drives check box (not displayed in screenshot) to perform an operating system only recovery (instead of a full system recovery).
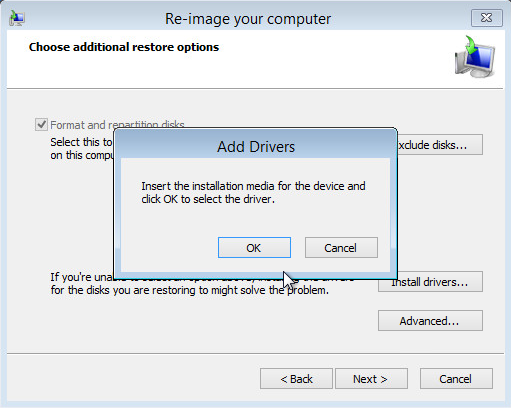
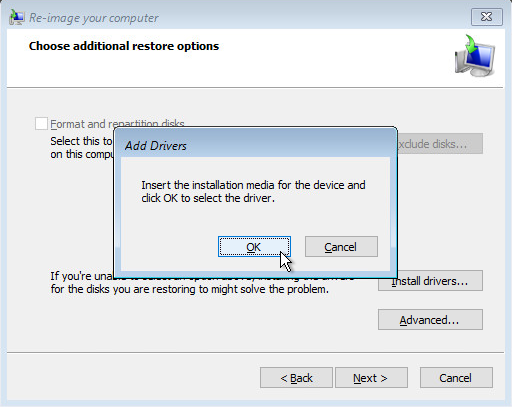
Click Install drivers to install device drivers for the hardware that you are recovering to.
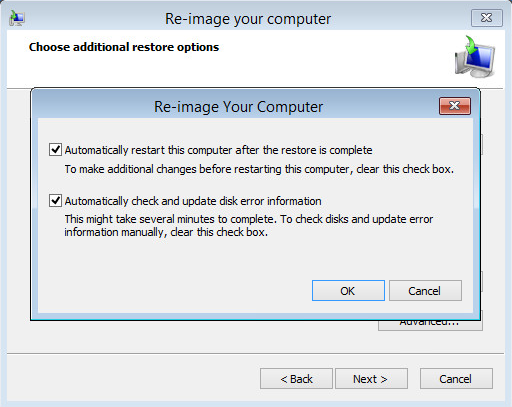
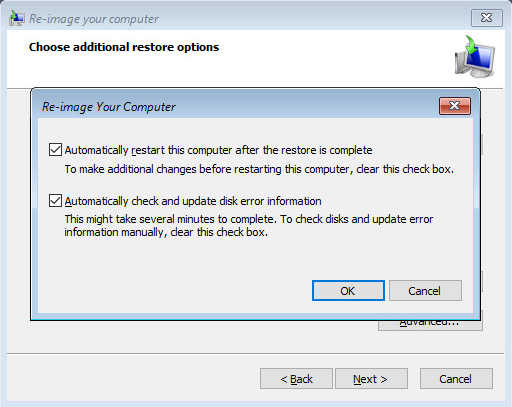
Click Advanced to specify whether the computer is automatically restarted, and the disks are checked for errors immediately after the recovery.
9. Confirm the details for the restoration, and then click Finish to start the recovery process.
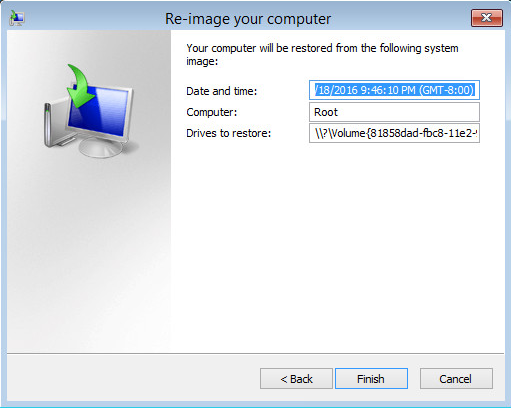
The recovery will succeed as long as all the critical volumes (e.g. volumes containing operating system components) are recovered.
If any data volume cannot be recovered, Windows will show a prompt with the un-recoverable volumes at the end of the recovery operation.
Recover a Full System (Non Server Platforms)
You can recover a full system using the advanced startup option by
- Starting Windows in safe mode
Press the Power button at the Windows login screen, in the Start menu, or in the Setting screen. Then press and hold the SHIFT key on the keyboard and click Restart.
Once you are in the Startup Option menu, perform the following steps.
3. Click System Image Recovery.
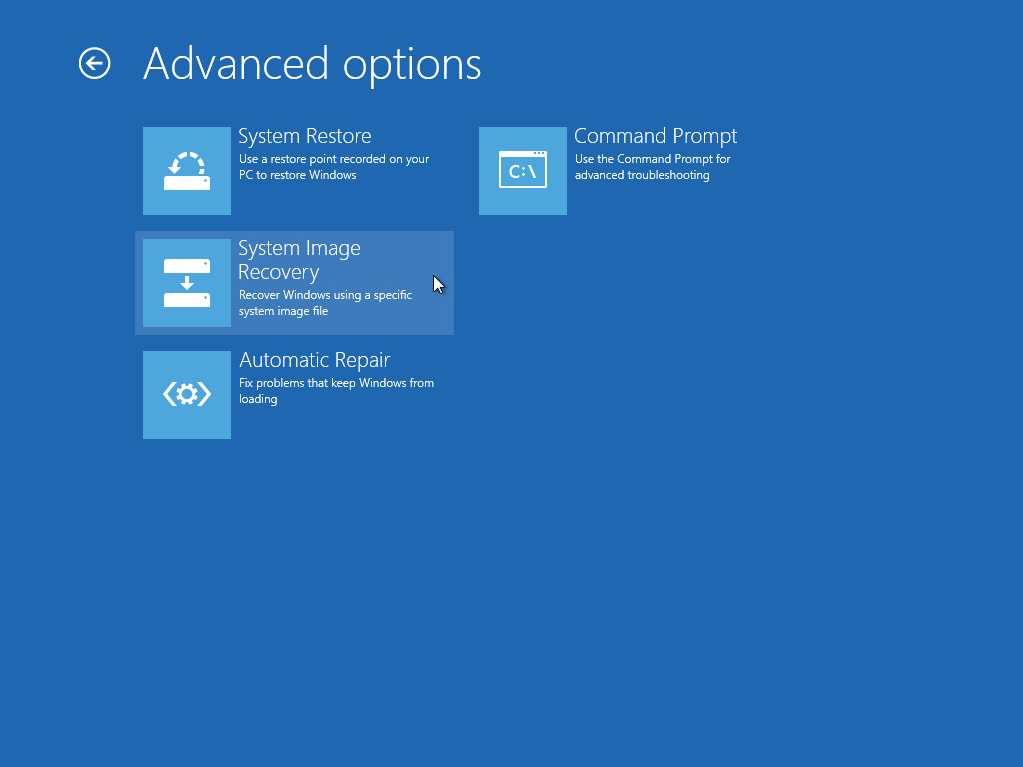
4. Login with an administrative account, by clicking on Administrator.

5. Click Select a system image, then click Next.
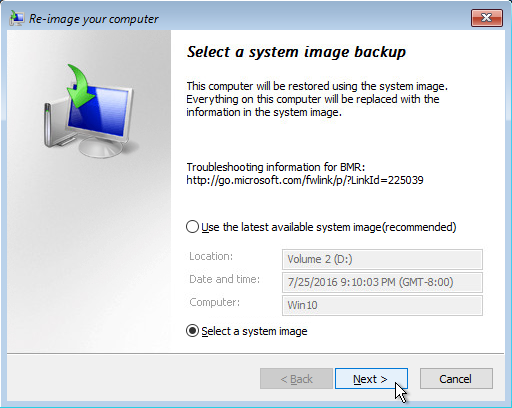
6. Select the location that contains the system image to restore from. If you do not see the image available, then
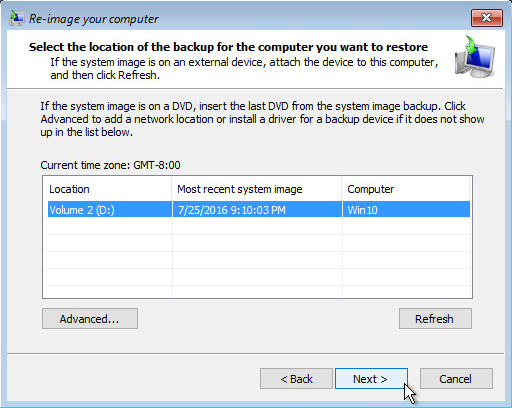
- Click Advanced, and install the required driver for the removable drive to be accessed, if the system image was copied to a removable drive attached to the server.
To install a driver, the driver must be located on the local system. You cannot install a driver from the network.
- Click Advanced, and browse to the remote shared folder which contains the system image, if the system image was copied to a network path.
For domain environment, if the backup storage location is on a computer that is a member of that domain, then the computer containing the storage location should be on the IPsec boundary, to be accessible by non-domain computer.
When a computer boots into Windows Recovery Environment, it becomes a non-domain computer, therefore, cannot access the usual network shares. Only those computers that allow non-domain computers to access the share can be used as a backup storage location in this way.
7. Select the date and time of system image to restore.
8. On the Choose additional restore options page.
Click Install drivers to install device drivers for the hardware that you are recovering to.
Click Advanced to specify whether the computer is automatically restarted, and the disks are checked for errors immediately after the recovery.
9. Confirm the details for the restoration, and then click Finish to start the recovery process.
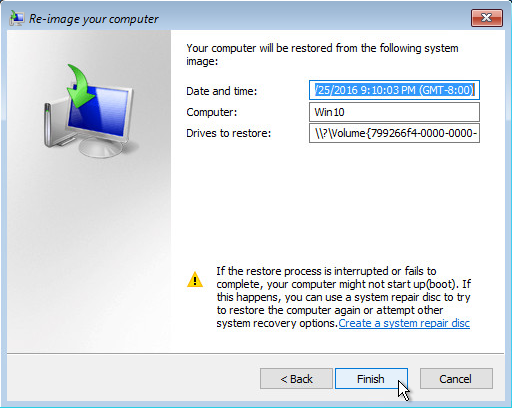
Do not interrupt the restore process.
The recovery will succeed as long as all the critical volumes (e.g. volumes containing operating system components) are recovered.